All the below links, excerpts, and pictures (charts/tables) are in English.
Japan-EU EPA 【Benefits and Backgrounds】(PDF; 07/2018) | MOFA Japan You can also check out the first one of the below pictures.
Japan-EU Strategic Partnership Agreement (SPA) (07/17/2018) | MOFA Japan
2018 Japan-EU Summit: Signing Ceremony Of EPA And SPA (YouTube)
The EU – Japan Economic Partnership Agreement (w PDF; 09/2018) | Policy Department for External Relations @ European Parliament (@Bruegel) You can also check out all the below pictures but the first one.
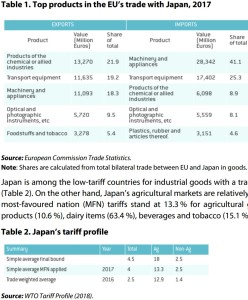
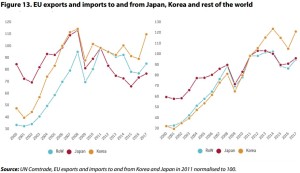
PDF p11 Within the EU-28, in 2017 the top goods exporters to Japan were Germany, Italy, the UK and France, respectively accounting for 32.87 %, 10.82 %, 10.67 % and 10.53 % of the EU’s EUR 60.66 billion of commodity exports to Japan in 2017. Germany, Italy, the UK and France were also the top four importers of Japanese goods, with respective shares of 23.28 %, 16.48 %, 14.37 % and 12.76 % of the EUR 68.89 billion worth of EU commodity imports from Japan in 2017.
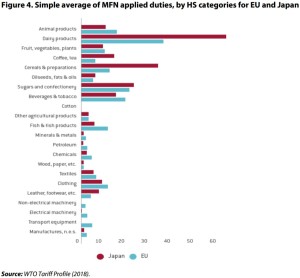
Japan is among the low-tariff countries for industrial goods with a trade-weighted tariff average of 1.4 % (Table 2). On the other hand, Japan’s agricultural markets are relatively protected. Simple average applied most-favoured nation (MFN) tariffs stand at 13.3 % for agricultural goods, with high tariffs on animal products (10.6 %), dairy items (63.4 %), beverages and tobacco (15.1 %).
Figure 4 depicts the EU’s and Japan’s tariffs by harmonised system (HS) product categories. In terms of the average applied MFN tariffs, we note that Japanese tariffs are low across numerous sectors such as electrical machinery (0.1 %), transport equipment (0) and manufactures not elsewhere specified (n.e.s) (1.2 %). Prominent exceptions are clothing (9 %), leather and footwear (7.7 %).
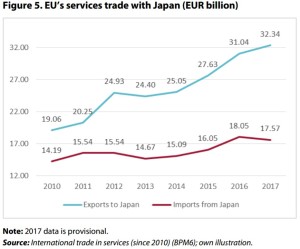
p12 The dominant sectors in the EU’s total service exports to Japan in 2016 were financial services (23.53 %), telecommunications (14.5 %) and transport (13.97 %).
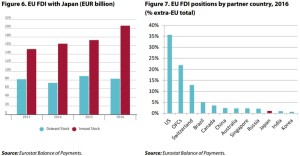
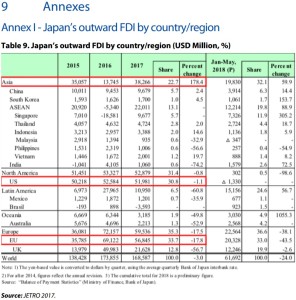
p13 Japan accounted for only 1.1 % of the total extra-EU FDI in 2016 (Figure 7). By comparison, EU investments in the US and Canada are much higher, representing 38 % and 3.7 % of total extra-EU FDI. Japanese investment in the EU stood at USD 56.8 billion, 33.7 % of its total FDI stock abroad in 2017. However, it should be noted that a substantial share, approximately 38 %, of Japan’s FDI stock in the EU is in the UK …
p15 A low score (0.05) in OECD’s FDI Regulatory Restrictiveness Index (2017), which measures statutory limitations on FDI, is indicative of the relative openness of the Japanese economy to foreign investors, as the OECD average is 0.07. On the other hand, the US (0.09), Canada (0.162) and China (0.316) are all relatively more restrictive as destinations for FDI. Except for a few countries in Europe (Austria, Poland and Sweden), all EU Member States are more open to FDI than Japan, with Luxembourg, Portugal and Slovenia being the least restrictive.
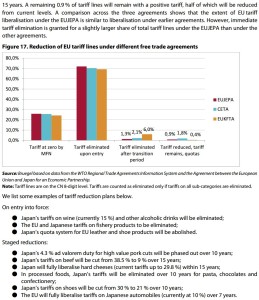
p17 Tariffs Agricultural goods. … significant reductions in customs duties for the EU’s major food exports to Japan such as pork (e.g. 4.3 % to 0 over 10 years for high value cuts), wine (15 % to 0 % on entry into force), beef (38.5 % to 9 % over 15 years), pasta and chocolates (complete tariff liberalisation in 10 years). For cheeses, the EUJEPA will deliver complete liberalisation for hard cheeses and provide tariff rate quotas (TRQs) with duty free access for fresh, processed and soft cheeses.
Industrial goods. In the agri-goods industry, South Korea was traditionally protectionist with a trade-weighted tariff of 49 % in the pre-FTA period. By 2014 however, these had been reduced on a preferential basis for EU goods to 28 %. The EU also liberalised its agricultural markets for South Korea by reducing trade-weighted tariffs from 11 % to 3 %.
Non-Tariff Barriers … Commission’s Impact Assessment Report (CIAR) in 2012 (European Commission, 2012). Japan is aligning itself with international standards on medical devices (Quality Management Systems), textile labelling (ISO international care labelling), motor vehicles (UNECE international vehicle regulations) and pharmaceuticals (ICH).
p18 Services The EUJEPA seeks to promote bilateral trade in a broad range of services but does not require governments to deregulate or privatise the provision of public services such as healthcare, water supply and education. … In telecommunications, the agreement covers issues such as mobile roaming, number portability and confidentiality of users’ traffic data. In financial services, the agreement calls for deeper regulatory cooperation and establishes a Joint Financial Regulatory Forum for this purpose. In e-commerce, the parties commit to keep electronic transmissions duty-free, recognise the legal validity of electronic contracts and signatures and may not require source codes to be transferred or accessed. In postal and courier services, the EUJEPA will attempt to build a level-playing field for EU suppliers and their main competitors such as Japan Post.
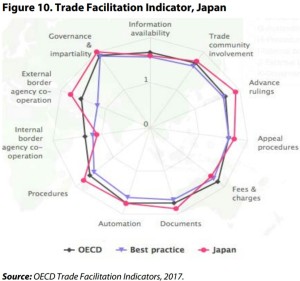
p21 Japan is one of the least restrictive economies in the world according to ECIPE’s Digital Trade Restrictiveness Index Report …
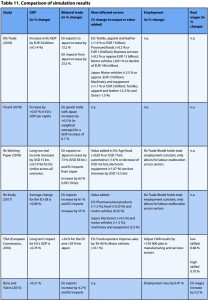
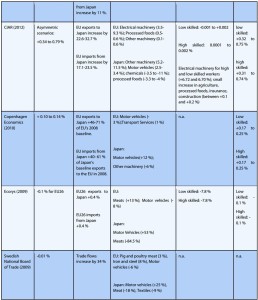
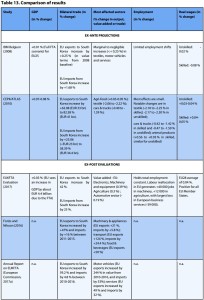
pp30-33 Bilateral trade There is substantial variation in the anticipated trade response. DG Trade (2018) found that the EUJEPA would lead to an increase of +13.2 % (EUR 13 billion) increase in EU exports to Japan. EU exports to Japan would rise by 22.6-32.7 % in the CIAR (2012) simulations. A much stronger export response for the EU is found in Ifo 2017 (61 %) and Ifo 2018 (73 %).
On the import side, DG Trade (2018) reports a 23.5 % (EUR 22 billion) increase in EU imports from Japan. This result is similar to that of CIAR (2012) which predicted increases in EU import purchases from Japan in the range of 17.1-23.5 %. In contrast, Ifo (2017) and Ifo (2018) simulations lead to increases in EU imports from Japan of 55 % and 63 %, respectively.
Sectoral value added All EUJEPA studies report a positive impact on value added in agri-food industries e.g.+0.82 % according to Ifo 2018, +0.2 % increase in output for processed foods in DG Trade (2018), 0.5-0.6 % for processed foods in the CIAR (2012) and +13 % for meats in Ecorys (2009). For automobiles, projections of value added are model-dependent.
By 2035, Japan’s car exports to EU increase by nearly 51 % in this study. Because of significant NTB reductions by Japan in motors, the EU also increases its exports to Japan following the EUJEPA (+11.5 %).
Textiles, apparel and leather products benefit from the agreement as well. The industry is expected to increase its output by 2 % (EUR 7 billion) in the EU, with exports to Japan rising by 220 % (EUR 5 billion) in DG Trade (2018).
Impact of Brexit Brexit has a greater impact on Japan, as it reduces the economic benefits from EUJEPA by 14 % (EUR 1 billion) and 20 % in Ifo 2017 and Ifo 2018, respectively. This is the result of a smaller market size for Japanese companies following Brexit.
Impact of CPTPP-11 Ratification of the CPTPP-11 agreement between Japan and 10 Pacific countries may also affect gains from EUJEPA. This scenario is evaluated in Ifo 2018. Simulation results reveal that the conclusion of the agreement leads to slightly smaller positive gains for the EU and slightly higher real-income gains for Japan (from 0.308 % to 0.314 %) compared to the simple baseline scenario. CPTPP-11 is expected to reduce Japan’s costs of sourcing inputs from the Asia-Pacific, improving its competitiveness and trade with the EU.
pp44-45 1/Investment liberalisation and promotion ISDS is the mechanism preferred by Japan, one that it has also supported under the CPTPP-11. In the investment negotiations held during July 2018, chief negotiators from the EU and Japan acknowledged the convergence of positions on investment protection standards but not on investor-state dispute settlement.
2/US investigation into auto imports … In March 2018, the US Department of Commerce initiated a National Security Investigation into the import of automobiles and auto parts into the US. This investigation is motivated by Section 232 of US’s Trade Expansion Act of 1962 and will examine whether declining American domestic production in the automobile sector poses a threat to its national security by weakening the internal economy and reducing domestic research on advanced technologies. Given the deep value chains in the auto industry, EU and Japanese car producers would be significantly harmed if the investigation leads to an increase in duties on foreign vehicles entering the US market.
On 25 July 2018, European Commission President Jean-Claude Juncker and US President Donald Trump announced plans to hold off on any new unilateral tariffs against each other as bilateral negotiations proceed on liberalising non-auto industrial goods, increasing EU imports of US soybeans and liquified natural gas (LNG), addressing WTO issues, reassessing US steel and aluminium tariffs and EU’s imposition of retaliatory tariffs on US goods. The EU will therefore be shielded from the conclusions of the US auto investigations, unless ongoing negotiations are halted by either party.
4/Tariff rate quotas (TRQs) … In the EUJEPA, Japan provides TRQs for agri-foods such as whey products, malt, potato starch, fresh and processed cheeses. …
5/Japan’s future trade ties with the UK … during the transition period (March 2019 to end of 2020). The exact terms of EUJEPA would hence be applicable to the UK over this period. Their implementation will be crucial for Japan’s car manufacturers that collectively produce 800 000 vehicles in the UK, accounting for 50 % of the UK’s total annual production …
In Focus EU-Japan ECONOMIC PARTNERSHIP AGREEMENT | European Commission
EU-Japan Economic Partnership Agreement: texts of the agreement | European Commission
EU-Japan: A Partnership of Renewed Importance (w PDF) | Cristina de Esperanza Picardo @eucentresg
New EU-Japan economic, strategic partnership may work better than past efforts (07/19/2018) | Bastian Harth @ Asia Times
… The SPA lays out the first-ever framework between the EU and Japan for cooperation and dialogue across various bilateral, regional, and multilateral issues such as cybercrime, disaster management, energy security, climate change, and aging populations. It also calls on both sides to synergize on promoting peace, stability, and international prosperity, and to recede from a sectoral and segmented approach to a comprehensive and legally binding cooperation framework. …
Especially, cybersecurity is of enormous importance for Japan, given the upcoming 2020 Tokyo Olympics. Millions of cyberattacks are predicted, and despite the country’s remarkable public safety… The topic is of such importance that Japan is even going to join the NATO Cooperative Cyber Defense Centre of Excellence in Tallinn. …
Brexit, a Catalyst for Closer EU-Japan Relations? (PDF) | Irina Angelescu
… Consequently, there is an implicit understanding from the Japanese side that the UK government “owes” special attention to Japanese interests, and should keep those interests in mind when negotiating Brexit. The former UK Ambassador to Japan, David Warren, indicated that some of his Japanese counterparts share a sense of “betrayal,” …
…three Japanese car manufacturers (Honda, Nissan and Toyota) now make almost half of the 1.67 million cars produced in the UK. …
… GlaxoSmithKline Plc estimates that, in the next two-three years, it could incur costs as high as 70 million pounds ($98 million) of Brexit-related costs. Similarly, Johnson & Johnson estimated that it could face as many as 50,000 additional tests in the amount of 1 million pounds if there will be no post-Brexit mutual recognition of testing between the EU and the UK. AstroZeneca and MerkKGaA raised similar concerns. …
… Mitsubishi Bank UFJ picked Amsterdam as its base for EU securities operations, while Nomura Holdings, Daiwa Securities and Sumitomo Matsui Financial Group said they would move to Frankfurt. …
… Decisions such as that of Unilever – the UK’s third largest company to consolidate its HQ in the Netherlands and abandon the separate London HQ is just one recent example that has caused more unease among third parties about the outcome of Brexit. …
The Japanese position has remained consistent about its preferences for Brexit from the very beginning: no Brexit or the “softest” form of Brexit, with unhindered access to the European Single Market – preferably preceded by a very long transition period that would allow Japanese businesses to adapt to changes. …
… In particular, joint training and cooperation to address newer threats like cybersecurity or disinformation campaigns conducted by countries like Russia and China could prove to be mutually beneficial. In principle, the U.S. should also welcome the closer economic ties between the EU and Japan as a means to promote free trade worldwide. At the same time, the EU-Japan data protection agreement and certain provisions in the EU-Japan EPA such as Geographic Indicators (GIs) for agricultural products could negatively affect U.S. interests. …
EU-Japan partnership agreements herald new era of closer cooperation (29/01/2018) | Irina Angelescu @ European Council on Foreign Relations
The EU-Japan Strategic Partnership Agreement (SPA): Good but Good Enough? (16/10/2018) | Axel Berkofsky @ ISPI
The EU-Japan Strategic Partnership Agreement (SPA) – Responding to the Crisis of the Liberal World Order (PDF; 12/2017) | Axel Berkofsky @ University of Pavia, Italy & Istituto per gli Studi di Politica Internazionale (ISPI) (@ Bertelsmann Stiftung) You can check out Table 1 and Figure 2 (in this PDF).
The EU-Japan EPA/SPA and the ‘Abe Doctrine’: Reinforcing Norms Globally, Changing them Domestically (PDF; 07/2018) | Edward Danks @ European Institute for Asian Studies
JAPAN-EU COOPERATION IN THE ERA OF INTERNATIONAL ORDER TRANSFORMATION: IN SEARCH OF A STABLE WORLD SYSTEM (w PDFs; 28/11/2017) | INSTITUTE FOR EUROPEAN STUDIES
EU-Japan Strategic Partnership Agreement (w PDFs) | Lords Select Committee, UK Parliament
EU-Japan Security Cooperation: trends and prospects (PDF; 07/03/2018) | The Royal Institute of International Affairs of Belgium & the University of Essex
EU-JAPAN – READY FOR A NEW STAGE IN RELATIONS? (PDF; Spring 2014) | Friends of Europe
The EU-Japan Strategic Partnership Agreement (SPA) – A Framework To Promote Shared Values [International Agreements In Progress] (12/10/2018) | Enrico D’Ambrogio @ European Parliamentary Research
Largest Bilateral Free Trade Agreement: Japan, EU Conclude Bilateral Economic Partnership Agreement (18/07/2018) | Ankit Panda @ The Diplomat