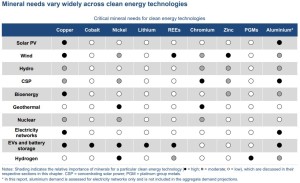
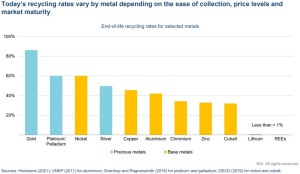
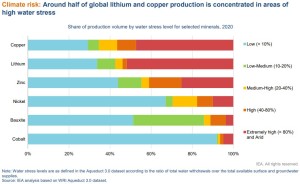
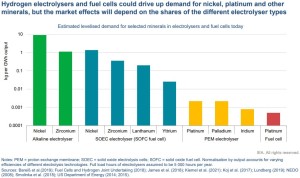
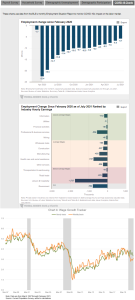
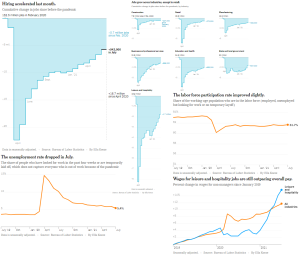
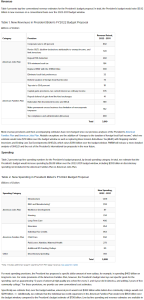
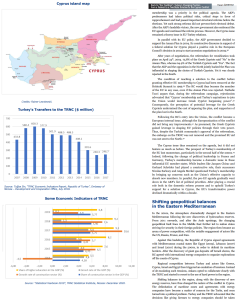
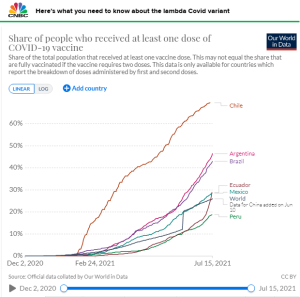
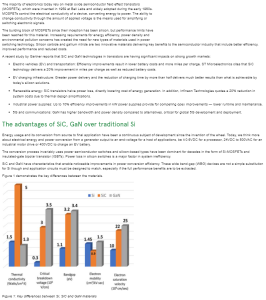
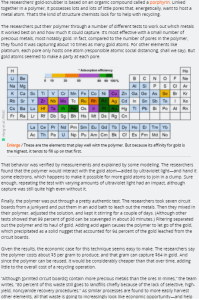
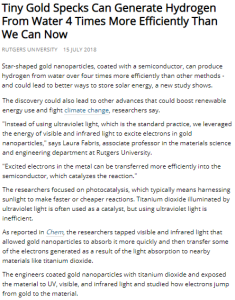
All the below links and tweets are in English.
取り急ぎ以下貼っておきます。
Science and Technology Vol.75 (phosphorus, graphite, etc.) リン、黒鉛など
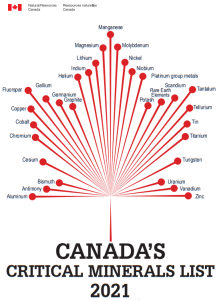
Science and Technology Vol.74 (manganese, etc.) / World Vol.163 (Australia, etc.) マンガンなど
Science and Technology Vol.73 (nickel, cobalt, lithium, etc.) ニッケル、コバルト、リチウムなど
Science and Technology Vol.72 (cobalt, etc.) コバルトなど
内容例(各回ツイートもご覧ください)
以下、順に、
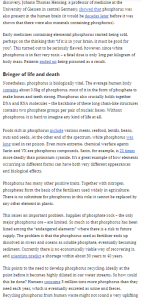
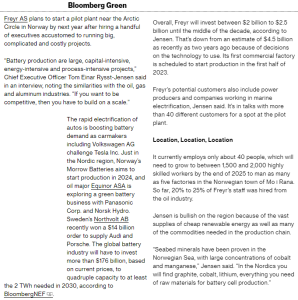
75:@Nanowerk、@scroll_in、@NRCan、@AlussaEnergy,@FREYRBattery,@climate
74:@MiningWeekly,@Element25Ltd、@BrookhavenLab,@LosAlamosNatLab
73:@IntEngineering、@ShefUniNews,@ChemistryWorld、@OxEconRecovery,@axios
72:@SaSpotters、@BYDCompany、@WIREDScience
71:@IEA,@CriticalMetals_
cobalt、lithium、nickel、manganese、graphite、phosphorusに関する日本関連ツイート
For cheaper hydrogen, just add cobalt: Japanese researchers have developed a new water-splitting technology based on a photoelectrochemical system made with titanium dioxide and cobalt. Cobalt is said to be a solid… https://t.co/OG2blGSVhx #solarenergy #solarpv #solar pic.twitter.com/eBrbGYPLUN
— pv magazine (@pvmagazine) February 19, 2020
TOKYO (Reuters) – Japan’s automakers aim to set up a joint procurement body by end-March to secure stable supplies of cobalt. https://t.co/GrBtE8tcpj #tsxvli #lithium #lithiuminvesting #preciousmetals #lithiumnevada https://t.co/8qAsB3XrHo
— American Lithium (@American_Li) August 11, 2018
Looking forward to hearing some news re: offtakes between Japanese OEMs & $JRV – cobalt has to come from somewhere.
Japan aims to electrify nation's new car fleet by mid-2030s https://t.co/SLenIaR27o
— Johnny Rainman (@MrJohnnyRainman) December 3, 2020
https://twitter.com/emil_jens/status/1144428802518343680
More @CBCNews on the Chemistry Prize, awarded to American, British and Japanese scientists who made the use of lithium ion batteries both possible and safe. https://t.co/w1wB1Ms1d3 pic.twitter.com/uwjdbhHRBC
— CBC News Alerts (@CBCAlerts) October 9, 2019
American, British and Japanese scientists who invented lithium batteries that power phones, laptops and tablets win Nobel Prize for Chemistry https://t.co/dk4EuHDV3a
— Daily Mail Online (@MailOnline) October 9, 2019
EGEB: Indiana energy-political corruption, Lithium Ion battery demand driving Japanese expansion, more https://t.co/GIjd94YSQu pic.twitter.com/TZIhNGpPX5
— Electrek.Co (@ElectrekCo) November 8, 2017
In Nobel speech, Japanese winner Akira Yoshino says #lithium-ion batteries will play key role in achieving sustainable society | The Japan Times https://t.co/fcwBqf9Dde
— Plateau Energy Metals Inc. (@pluenergy) December 9, 2019
Good article by Gerrit, confirms importance of Japanese customers..
Lithium Pricing 2019: encounter an old pattern?https://t.co/oxSvSW753G— Argosy Minerals Ltd (@ArgosyMinerals) February 6, 2020
US based Triton Electric Vehicle to set up #manufacturing facility in Gujarat. While Japanese cos Suzuki, Toshiba and Dentsu have all already set up lithium #battery unit in the state#ElectricVehicles #ElectricCars #Gujarat #industrial https://t.co/lcgW7qp5tm
— Hiren (@BHiren) June 23, 2021
EVERYWAY4ALL Electrode Pads
Use SEKISUI Japanese gel, which is nickel-free, dye-free and latex-free, with spunlace non-woven cloth that enhances the softness of the electrode and makes it be highly stretchable and flexible. pic.twitter.com/EHzJTUO2Mv— EVERYWAY4ALL (@Everyway4A) November 5, 2020
#Toyota coming around on #EVs. Hybrids not going to cut it long-term; plus Toyota acknowledge they will be short EV batteries; will partner with various Chinese (CATL, BYD) & Japanese battery and EV manufacturers. #batteryminerals #batterymetals #lithium #cobalt #graphite #nickel https://t.co/dZ6QwKWxPV
— David Anonychuk (@DavidAnonychuk) June 7, 2019
Here is a meal that helps keep wrinkles away!!! A delicious curry high in antioxidants (from Japanese sweet potatoes) collagen formation properties (from shishito peppers) and natural sunblock from manganese (garbanzo beans), this meal tastes fantastic and is #vegan #glutenfree pic.twitter.com/rzOM7Lgnvu
— Violet Alexandre (@lvdreamer) March 14, 2018
Two sake cups found in Tokyo and Masakatsu – white tin glaze with manganese edge, not so different from Lucie Rie tea cups and cream crazed glaze over 100 yrs old. #handmade #ceramic #simplicity #japanese pic.twitter.com/7I9aEufbR3
— ClayworksLondon (@ClayworksL) September 12, 2018
https://twitter.com/1444552ari/status/1291234019200208898
This is a 5 fen coin from 1945 from the Japanese puppet state of Manchoukuo in northeast China & inner Mongolia. The state existed from 1932 to 1945 with limited international recognition. This coin is made of Magnesite (MgCO₃), a mineral with Iron, manganese, cobalt and nickel. pic.twitter.com/sv4OkqLXW8
— Coin of Note (@CoinOfNote) June 19, 2019
Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association (Jama) had said high manganese content in petrol was causing health hazard and engine problems https://t.co/vNTKDhXcsq
— Dawn.com (@dawn_com) May 26, 2018
https://twitter.com/yonexgolf_uk/status/1105144087441747969
.@yonexgolf_uk is proud to announce the launch of the new EZONE GS (Graphite Speed), a stunning range of #Golf clubs, inspired by Japanese graphite technology, designed to offer superior distance and control for mid handicap golfers.
More here: https://t.co/lfPCgDZeJH pic.twitter.com/oH6Ob2yCZi
— Women & Golf (@Women_and_Golf) January 16, 2020
J.M.M. THE NOKONA: GRAPHITE. PART 2.⠀
➖⠀
The Nokona in Graphite, handcrafted in Japan. A limited production batch of 500 pieces.
Available on https://t.co/yOmJx0HYSG
➖⠀#JacquesMarieMage #EmbraceTheSpectacle #TheNokona #NokonaGraphite pic.twitter.com/sko9kb2bag— JacquesMarieMage (@JMarieMage) November 5, 2020
The world’s first zero-emission tanker is to be built in Japan by mid-2021, powered entirely by batteries.#seatransport #Japan #electricships #batteries #batterymetal #graphite #KatengezaGraphite $4ce #Malawi #Africa
https://t.co/FjbBJYRj8I via @technology
— Graphite Africa (@AfricaGraphite) August 8, 2019
The HTTR is back. It's a graphite-moderated gas-cooled reactor in Japan with an incredibly high outlet temperature approaching 1000 °C (enabling many process heat applications typically out of nuclear's range). https://t.co/W0iib5hiVv
— Nick Touran (@whatisnuclear) July 30, 2021
Graphite Players in focus
– Every 1MMT of Electric Arc Furnace implies additional demand of 2500MT of Graphite Electrode
– Japan biggest player of GE (54% share) with India at 23%
– Currently, 19 plants in 15 countries working at 85-90% capacity@CNBCTV18Live @ETNOWlive pic.twitter.com/zP1yBtFdqH— Toshniwal Equity (@ToshniwalEquity) September 23, 2019
https://twitter.com/man_integrated/status/1390772764982796295
Tokai Carbon, a Japanese graphite electrodes producer raised its electrodes contract prices for H1CY19. @Nigel__DSouza tells us the reason why graphite stocks are surging in trade pic.twitter.com/wZAFxrTfeS
— CNBC-TV18 (@CNBCTV18News) January 16, 2019
With its beautiful photography and subtle typographic elements, #DentsuJapan's posters for Japanese haircare brand #Eral was a judge favourite at D&AD Awards this year. It won a Yellow Pencil in #Photography & Graphite in #GraphicDesign. #dandad20 pic.twitter.com/dcb6yPccAB
— D&AD (@dandad) November 12, 2020
On 11 March 2011, a 16.7-meter tsunami wave surged over the Iwate Prefecture in Japan. This Graphite Pencil-winning campaign by HAKUHODO Kettle/Hakuhodo for @Yahoo served as a visual reminder of just how high that wave was. Check out the video, here -> https://t.co/Aj44aSRNhG pic.twitter.com/pqn5TQp0O8
— D&AD (@dandad) May 15, 2018
Pocky sticks have been Japan’s top-selling snack for decades. This stylish new packaging by @dentsuaegis is minimal yet playful and features a palette of vibrant, popping colours. It won Graphite Pencil for #Branding at #dandad20 pic.twitter.com/gsUA6ilwTt
— D&AD (@dandad) August 10, 2020
Offtake MOU with leading Japanese trading company Hanwa Corporation. Renascor's third offtake agreement for our #battery #anode materials project in #SouthAustralia. Link: https://t.co/MFTWruLM1Q #graphite #criticalminerals #lithiumion #ESGinvesting #CleanEnergy #RNU $RNU. pic.twitter.com/128D3pa8vl
— Renascor (@Renascor_ASX) March 24, 2021
A cult favorite among illustrators, @Blackwing Pencils are great for drawing, lettering, scoring music, even everyday use! Premium Japanese graphite leads include clay (for strength) and wax (for smoothness). Semi-hexagonal shape, unique flat erasers. https://t.co/AkecHtrDUd #art pic.twitter.com/2kgA8u9yCb
— Blick Art Materials (@Blick_Art) November 1, 2018
Made from Californian incense cedar wood and high quality Japanese graphite leads, our Palomino Blackwing pencils are crafted with an exceptional balance of softness, darkness, and sharpness ✏️ pic.twitter.com/3Em6i7Qe8k
— Papersmiths (@paper_smiths) February 26, 2019
These are the best Japanese pencils you can by. The graphite is firm, but writes dark and buttery. The eraser is truly excellent. And the color reminds me of the Hankyu trains, my favorite trains in Japan. Highly recommended ✏️ pic.twitter.com/HLqNWxh9Q6
— Brian Ashcraft (@Brian_Ashcraft) April 26, 2020
NextSource Materials (TSX:NEXT) has signed an offtake deal with a “prominent” Japanese trading company that supplies flake graphite to a major Japanese electric vehicle anode producer. https://t.co/uZ00X7mAdb #criticalmetals #graphite #investing
— Resource Investing (@INN_Resource) October 17, 2018
Since @Tirupatiuk's MoU with Hanwa – a major Japanese trading and investment biz – #TGR's SP has inexplicably fallen 12%.
The MoU has already generated "initial discussions with prospective buyers" in the Far East over TGR's graphite products from both Madagascar and India.
— Myles McNulty (@MylesMcNulty) July 13, 2021
https://twitter.com/MrGraphite2/status/1111821592856715264
Hanwa, listed on the Tokyo stock exchange (TYO:8078, Mkt cap ¥137.58 billion/GBP 1.18 billion), is a leading Japan-based global trading and investment company and one of the larger traders of battery chemicals and steel products in the Asian region #TGR #Graphite #Graphene pic.twitter.com/xXm0edACmv
— Tirupati Graphite (@Tirupatiuk) July 6, 2021
https://twitter.com/GANYACINEMAART/status/1135922438699716608
M u s i c x d r a w i n g .
I can't get you off my mind.
Music score: "Lost in Japan | @ShawnMendes "
Graphite on 6x9in. watercolor paper. pic.twitter.com/fLnlHBAjj0— Sq (@s_q_d_d) November 20, 2018
*
*
『 Vanitas 25 』
Hiroshi Hayakawa 2021Graphite and colored pencils on Bristol board
[ 18x13 in ]#HiroshiHayakawa#PrivateCollection
Hiroshi Hayakawa HPhttps://t.co/lUab3U9xLm pic.twitter.com/c3gIFmrhQz— ** IKUMI ** (@_Japan_Sapporo_) August 11, 2021
#Benchmark2019 World Tour – Australia, S Korea, Japan, Hong Kong – next 3 weeks!
My presentation: Culture Clash between Autos-Batteries-Mining
Join us for free below: https://t.co/KZE88AIaMt #lithium #cobalt #graphite #nickel #EV
— Simon Moores (@sdmoores) September 9, 2019
China’s BYD and CATL eye Japanese storage battery market. https://t.co/06I5itMesz via @NAR @BYDCompany #BYD #CATL #China #Japan #batterystorage #batteries #batterymetal #graphite #GraphiteAfrica $4ce #mining #Malawi #Africa
— Graphite Africa (@AfricaGraphite) September 2, 2019
Chicken manure is a high-quality organic fertiliser, which contains about 1.63% nitrogen, 1.54% phosphorus, and 0.85% potassium. ZCME have decided to utilise this useful resource and establish a chicken manure pelleting project in Sendai, Japan.https://t.co/BQnf0G4Sbc pic.twitter.com/r6ZX7dnPzz
— Global Miller (@MillingandGrain) July 28, 2020
Researchers from #IHeartNatSci and the RIKEN Nishina Center in Japan discovered eight new rare isotopes of the elements phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, argon, potassium, scandium and calcium. These are the heaviest isotopes of these elements ever found. https://t.co/8cbLhPk083 pic.twitter.com/XM6SwHEwQG
— MSU Natural Science (@MSUNatSci) July 12, 2018
Researchers from @MichiganStateU and the @RIBF in Japan discovered eight new rare #isotopes of the #elements #phosphorus, #sulfur, #chlorine, #argon, #potassium, #scandium and, most importantly, #calcium. @NSF https://t.co/ynFtCtBY36 pic.twitter.com/ieK4P6Kt1z
— KualiResearch (@KualiResearch) July 22, 2018
We’re launching Axtra® PHY, the latest generation of phytase enzyme, in Japan. Our phytase enzyme is the fastest route to helping producers improve animal performance, while improving profitability and #sustainability by reducing phosphorus waste. https://t.co/NjslKWsps4
— Biobased (@DuPontBiobased) September 12, 2019
A healthy #diet is a varied diet! WFP delivers Japanese tuna to families in #Gaza to ensure their intake of protein & phosphorus pic.twitter.com/d5NxQaanMZ
— World Food Programme (@WFP) December 31, 2016
7. YOGURT: Yogurt is rich in calcium, potassium, phosphorus, and selenium. A study in Japanese adults found that higher intakes of calcium, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium were associated with increased lung function markers.
It's best to make lungs strong. pic.twitter.com/8y9nSPVfBG— चेतन्य राजपूत (@RAJPOOT55532237) May 7, 2021
Congratulations to @ACESIllinois International Graduate Grant recipient Yuhei Nakayama @IllinoisCropSci for “Optimizing a biochemical tool to enable global evaluation of #phosphorus recycling in #agroecosystems using Japanese volcanic soils” advised by @ajmargenot #Japan #soil
— ACES International (@ACES_OIP) April 24, 2019
A method to anaerobically disinfect soil to increase phosphorus using diluted ethanol – +GENERAL PHYSICS LABORATORY (GPL)
Scientists in Japan and the Netherlands have independently developed anaerobic soil disinfestation, also known as …https://t.co/rilBLn04MB
— General Physics Lab (@genphys) June 15, 2020
Japan will launch its research assistance programme in Nepal's agriculture sector by implementing phosphorus-efficient paddy.https://t.co/2miZmX06hg — by @sangamprasai
— The Kathmandu Post (@kathmandupost) November 14, 2019
Recovery, reuse of phosphorus from wastewater – The Japan Times https://t.co/h1fCMJdFWC pic.twitter.com/0Nuz2Ny6W8
— Petrolec (@PetrolecSocial) September 14, 2018
A Japanese study which is conducted for recovery of phosphorus (P) and potassium (K) as struvite-K (KMgPO4•6H2O) #precipitates confirms that recovery of biomass incinerated is successful as struvite-K and can be used as fertilizers.
More @ https://t.co/3l28XAl64j pic.twitter.com/4xGsWlgUVj
— Scirp Papers (@Scirp_Papers) August 16, 2021
@AgInstituteAus director Daniel Tan spent some time in Japan recently – a discussion on remote sensing of nitrogen and phosphorus in crop plants with Professor Toru Fujiwara from @UTokyo_News_en was just one of his visits! pic.twitter.com/rJkGq0O86b
— Ag Institute Aus (@AgInstituteAus) May 8, 2018
MIPT scientists and their colleagues from Japan and the U.S. have calculated the parameters of photodetectors comprised by layers of #graphene and a combination of black phosphorus and black arsenic. @univ_aizu, @TohokuUniPR, @UBuffalo, @rpi
Read more: https://t.co/hZerDEscJg pic.twitter.com/VBv2aS1K7J
— MIPT — Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology (@mipt_eng) April 14, 2020
#SuperfoodSaturdays… Native to Taiwan and Japan, this superfood "Chlorella" is rich with phytonutrients, including amino acids, chlorophyll, beta-carotene, potassium, phosphorus, biotin, magnesium and the B-complex vitamins.
Chlorella is a blue-green algae like its cousin… pic.twitter.com/pwxHXlZfzn— Davinder Ojalla (@davinderojalla) January 12, 2019
2️⃣ Persimmon contains vitamins A, C, E, and B6, as well as dietary fiber, manganese, copper, magnesium, potassium, and phosphorus.
3️⃣ Although native to China, Persimmon is the national fruit of Japan, where it's widely cultivated and enjoyed by many.
— Secrets Of The Tribe (@secrets_tribe) July 5, 2019
The unit removed a total of 14 devices from the island including a 90mm high explosive projectile, two 105 mm white phosphorus shells and three Imperial Japanese anti-boat mines.https://t.co/NMxpsWMnJD pic.twitter.com/LWPK0W3OJM
— Military Times (@MilitaryTimes) September 1, 2020
a great day and saved million of Japanese , as they were going to fight on tell the last man .is dead . the war would of gone on for 3 more years as we surround the island and used are 16 inch guns and phosphorus bombs night and day , then million dead .Japan had no Navy or air . https://t.co/irQY5Elfb6
— Chris (@ChristopherCud1) August 6, 2018
Men of a Sikh regiment clear a Japanese foxhole at Mandalay with machine gun fire after throwing in a phosphorus grenade, 1945. #WW2 pic.twitter.com/BULsv95gb0
— WWII Pictures (@WWIIpix) October 10, 2018
Amazing Military Stories
1/7. On April 12, 1945 Staff Sgt. Henry R. Erwin was a radio operator aboard a B29 flying a bombing run over Japan. Upon reaching the target area, a white phosphorus canister ignited inside the bomb bay of the aircraft. pic.twitter.com/OtdaDgD9hx— Irish Warrior (@VeteranIrish) July 15, 2021
#OnThisDay #OTD the u.s dropped burning white phosphorus and napalm on Tokyo, Japan, killing over 100,000 in what has been called "the deadliest air raid in #history." May the victims of imperialist wars find peace in the afterlife. pic.twitter.com/YjMrNQu1JH
— Steve Lalla (@steve_lalla) March 9, 2021